Bad Generalization & Overfitting
Bad Generalization : low $E_{in}$ and high $E_{out}$
Overfitting : lower $E_{in}$ and higher $E_{out}$
Cause of Overfitting : use excessive $d_{vc}$ , boise & limited data size $N$ .
The Role of Noise & Data Size $N$
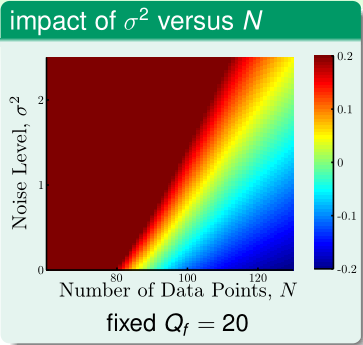
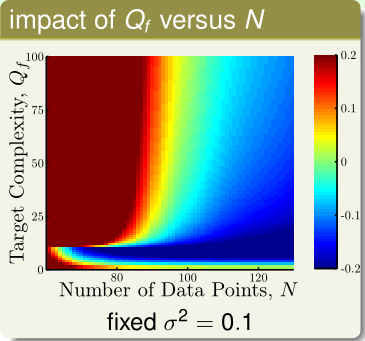
当 $N$ 较小时,很容易发生过拟合,再加上 noise 的作用,模型可能为了拟合 noise 使得 $E_{in}$ 降下来. 此外,目标函数的复杂度也会对过拟合现象发生产生影响.
需要注意的是在图2底端,对应于目标函数过于简单的情况也比较容易发生过拟合,因为使用更复杂的模型去拟合更简单的目标函数很容易过拟合.
four reasons of serious overfitting :
data size $N\ \downarrow$
stochastic noise $\uparrow$
deterministic noise $\uparrow$
excessive power $\uparrow$
当 $f$ 不在假设空间 $H$ 中时,某些 $f$ 的部分不能够被 $H$ 捕捉. deterministic noise 描述了 difference between best $h^*\epsilon H$ and $f$ .
Dealing with Overfitting
- start from simple model
- data cleaning/pruning
- data hinting
- regularization
- validation
Data cleaning/pruning :
if ‘detect’ (hard part) the outlier by : too close to different classed samples, or too far from same classed samples ; wrong by current classifier ; …
- possible action 1 : correct the label (data cleaning)
- possible action 2 : remove the example (data pruning)
(possibly helps , but effect varies)
Data hinting :
add virtual examples by slightly shifted/rotated digits carry the same meaning
(possibly helps, but watch out —> virtual example not $\mathop{\sim}\limits^{i.i.d}P(x,y)$ !)